Introduction
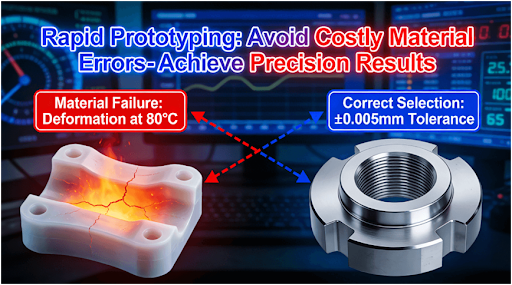
In the hurried world of product development, material choice mistakesin rapid prototyping are quite common and prove to be a pricey mistake because prototypes may fail or projects may get delayed and go over budget. For example, when plastics are not selected based on the ambient temperature and are subjected to high temperatures, they may deform or fail because metal may fatigue and fail because traditional methods lack a scientific approach to handle project requirements.
This article, citing best practices in the sector as well as best available standards, lists a definitive framework for materials selection, whereby the pitfalls described above may be avoided. The underlying principles of materials science may be utilized in the design of products so that the chances of a rapid prototype project failing may be eliminated. Moving on to the topic, the description begins, introducing the relevant terms such as Rapid Prototyping Services.
Why Is Material Selection the Foundation of Successful Rapid Prototyping?
Materials to use act as the vital determinantof rapid prototyping, thereby affecting the functionality of the prototype, the validity of the prototype test, as well as the cost involved. Sometimes, a bad choice may halt the most brilliant designs.
How Material Properties Affect the Performance of a Prototype
Material properties, such as tensile strengthand thermal resistance, determine a prototype’s behavior in real-world conditions. For example, a material that has poor fatigue resistance may make an aerospace structure fail catastrophically during a stress test. Statistics have shown that material-related mistakes are responsible for around 30% of prototype failure. This illustrates the proper importance of accurate selection. Matching application demand by material characteristics allows the developer to achieve authentic end-use performance simulation through prototypes.
Case Study: Results of One-Dimensional Thinking – Neglect of the Environment
A practical example concerning a car element shows that under real humidity and variation in temperature, the warping of polymer-based prototypesresulted in inaccurate testing and costly redesign. This demonstrates how operational conditions should be considered at the selection stage. Using scientific approaches, such as lifecycle analysis, can prevent these issues by reviewing material behavior under a wide range of scenarios and reducing risk accordingly.
The Role of Data-Driven Decision-Making
Adopting a data-driven approachallows leveraging from historical performance data and predictive modeling to minimize informed guesswork. Materials databases linked to CAD allow engineers to base comparisons on empirical evidence, with fewer opportunities for making errors. These procedures enhance reliability and also maintain adherence to industry benchmark standards, allowing for further discussion of standards in the following sections.
What are the major options for materials for each of the rapid prototyping processes?
Understanding the interplay between materials and processesis vital to effectively optimize rapid prototyping. The following section covers typical materials—such as thermoplastics, resins, and metals — and their compatibility with different methods of FDM, SLA, and CNC machining.
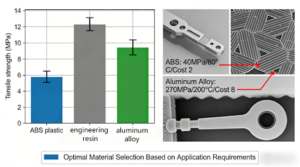
Thermoplastics and FDM: Cost and Functionality: Thermoplastics such as ABS and PLAare widely preferred in FDM because of their relatively low cost. However, they may not be strong enough to endure functional testing. On the contrary, PEEK is stronger compared to thermoplastics yet costs more. A comparison table (for example, material vs. process matrix) can be very helpful to developers in taking informed decisions on various considerations such as mechanical strength.
l Resins and SLA: Precision for Detailed Prototypes: SLA resins are great when a high-resolution part with a smooth surface is desired, such as a visual model or a medical model. However, SLA resin is brittle and doesn’t have good heat stability, which can make it unsuitable for functional models despite its strengths in creating prototypes. Engineers must consider criteria such as UV Resistanceor Biocompatibility, which can lead to mismatches in requirements and make a customized selection guidenecessary.
l Metals and CNC Machining: Building Resilience for Critical Tasks: Metal prototypes through CNC machining offer unprecedented robustness to withstand various environmental conditions. Aluminum or titanium alloysare strong materials that demonstrate a highly favorable strength-to-weight ratio. In this regard, it may be noted that working costs and time are also to be taken into account. For further clarification on this point, readers are directed to appropriate technical literature available from cost-effective custom rapid prototype serviceproviders.
How Can Engineers Choose Materials for Complex Part Designs?
In complex geometrical shapes like commercial or medical applications or robotics, a sensitive method should be used for material selection. In this section, a decision-making process is described that is centered on mechanical requirements, environment resistance, and regulations.
Handling Multi-Material & Geometric Complexity
Compliant part geometries may require assembling multiple materials or dealing with complex geometric features that have features such as thin walls. For example, grippers for robotic surgery need to provide both the required strength for grasping and biocompatibility. By taking a structured approach to assess variables that impact design, failures can be prevented.
Certification Utilization in Quality Assurance
Certifications, such as ISO 9001, are industry standards that form the basis of some level of guarantee of quality. Suppliers who meet these standards are able to deliver material that has a guaranteed quality, which is of high importance when working within a specifically controlled industry.
Early Integration with DFM Principles
The principles for Design for Manufacturability, or dfm, act to encourage material selection that takes into consideration the production limitations, thereby reducing the iterations. The following are examples of such considerations: the selection of material compatible with the production process via 5-axis CNC machining, which can be used for the production of complex shapes.
What Role Does Cost-Benefit Analysis Play in Material Selection?
A thorough cost-benefit analysisgoes beyond the cost of material to incorporate less obvious expenses such as processing time and scrap rates. This is examined further in the following outline for tiered financing.
Evaluating Direct vs. Indirect Costs
The costs associated with direct material are quite apparent; however, some indirect aspects, like the time involved in machining or disposal costs, may play a substantial role in determining overall costs. Consider the example wherein a less expensive polymer material requires higher print time due to labor costs.
Stratification by Prototype Stage
Prototypes of research concepts tend to work well with materials such as PLA, while functional prototypes require high-performance materials such as nylon composites. Data suggests that utilization of advanced materials during testing stages may cut future costs associated with redesigns by a considerable 20%.
Leverage Tools for Economic Optimization
Software that allows the calculation of the cost of ownershiphelps estimate the savings. Parameters such as volume and tolerance can be inserted to compare the different materials. Therefore, the choice of materials is both technically and economically correct.
Industry Standards and Precision Tolerances in Ensuring Quality in Prototyping
ASME Y14.5 standardsand ISO certifications are of key importance in achieving accuracy in prototyping. This part of the report will examine how they reduce discrepancies.
The Importance of Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T)
The standards of GD&T, like ASME Y14.5, offer a common language for describing tolerancing to guarantee that the designed part is attained. For instance, a tightly toleranced part (±0.005mm) avoids assembly problems in automotive parts.
Case Study: Tolerance Failures and Corrective Actions
A scenario of an imprecisely fitted drone part illustrates the issues arising from tolerance deviation and failures in drone functionality. Through the application of operational protocols, issues may be quickly resolved, pointing to the importance of documentation and audits.
aligning with ISO for Continuous Improvement
ISO 9001 certificationpromotes a culture of improvement. This is achieved through regular audits. This not only enhances quality but also enhances customer confidence in an organization. ISO promotes customer confidence.
What Future Trends Are Revolutionizing Rapid Prototyping Materials?
Smart materials innovationand sustainability are changing the scenario in prototyping. Trends such as self-healing polymers, bio-based composites are emerging in this field.
- The Emergence and Development of Smart and Adaptive Materials: Intelligent materials that react to environmental changes, such as temperature-sensitive alloys, allow the creation of prototypes with dynamic functions. These developments open up the field of prototyping to technological innovations like the IoT sector.
- Sustainable Materials Reducing Environmental Footprint: Biodegradable plastics/polymersand recyclable metals are becoming more widely used owing to the eco-friendliness that they offer. For instance, PLA, which is manually processed, is more eco-friendly since it emits fewer pollutants with no effects on performance properties. This is because it conforms to the international standards of ISO 14001.
- The Integration of AI and Predictive Analytics: AI-based toolsare transforming material choices through predictive capabilities based on performance conditions. The tools utilize large sets of data to direct designers to the best material choices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, material strategyis the determiner for the successful execution of rapid prototyping, as it will help the developers avoid any limiting factors by optimizing the project output accordingly. In the coming future, it is essential for all sectors to focus on trends as it will help them retain their utmost superiority.
FAQs
Q: What is the commonest mistake concerning materials used in rapid prototyping?
A:Use of generic plasticsfor high-temperature purposes, leading to the deformation of plastics. A science-based material selection resource, like the use of ISO materials, can eliminate this problem by associating materials with their environments.
Q: How Can I Get a Good Quote for Prototype Development?
A:Detailed CAD drawingsand specifications. A good supplier should be able to provide automated quoting capability depending on the chosen materials.
Q: Are there eco-friendly alternatives for prototype materials?
A:Yes; biodegradable polymersas well as recycled metals are on the upsurge. They are more environment-friendly without compromising on functionality. They are supportive of initiatives like ISO14001.
Q: What are some certifications to look for in a prototyping partner?
A:First, follow ISO 9001for quality management issues. Then follow AS9100D in aerospace standards. These are important for having proper processes in place.
Q: How do tolerances impact the cost of a prototype?
A:More precise tolerances (e.g., ±0.005mm) are expensive, requiring better equipment, so the need for such tolerances in a functional prototype might be less, depending on the application.
Author Bio
The writer is a subject matter expert in precision manufacturingand works with or is affiliated with LS Manufacturing. The company assists engineers and research scholars in dealing with difficult part tasks in aerospace, medical, or automotive industries by providing rapid prototyping serviceswith a focus on quality. The company includes quality certifications like ISO 9001, AS9100D, and IATF 16949 with its credentials and guarantees excellent work through DFM or free project review by contacting them immediately.